Base64 Algorithm
Introduction
-----> Base64 encoding is used to convert binary data into a text-like format that allows it to be transported in environments that can handle only text safely.
-----> Base64 is sometimes also refered to as PEM, which stands for Privacy-enhanced Electronic Mail. There, Base64 was used to create printable text again after binary e-mail data that was generated during the e-mail encryption process.
How it works
Base64 encoding takes the original binary data and operates on it by dividing it into tokens of three bytes. A byte consists of eight bits, so Base64 takes 24bits in total. These 3 bytes are then converted into four printable characters from the ASCII standard.
The first step is to take the three bytes (24bit) of binary data and
split it into four numbers of six bits. Because the ASCII standard
defines the use of seven bits, Base64 only uses 6 bits (corresponding to
2^6 = 64 characters) to ensure the encoded data is printable and none
of the special characters available in ASCII are used. The algorithm's
name Base64 comes from the use of these 64 ASCII characters. The ASCII
characters used for Base64 are the numbers 0-9, the alphabets 26
lowercase and 26 uppercase characters plus two extra characters '+' and
'/'.
In our programs, we can simply define this table as a character array. For example in 'C' we will do:
/* ---- Base64 Encoding/Decoding Table --- */
char b64[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/";The ASCII conversion of 3-byte, 24-bit groups is repeated until the whole sequence of original data bytes is encoded. To ensure the encoded data can be properly printed , newline characters are inserted to keep line lengths below 76 characters.
Example
Let's say we want to convert three bytes 155, 162 and 233. The corresponding 24-bit stream is 100110111010001011101001.
155 -> 10011011
162 -> 10100010
233 -> 11101001
Splitting up these bits into 4 groups of 6bit creates the following 4 decimal values: 38, 58, 11 and 41.
100110 -> 38
111010 -> 58
001011 -> 11
101001 -> 41
Converting these into ASCII characters using the Base64 encoding table translates them into the ASCII sequence "m6Lp".
38 -> m
58 -> 6
11 -> L
41 -> p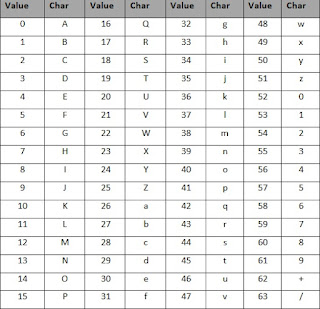

Mass daaa..maamee💓😍💥😎
ReplyDelete